These cybersecurity statistics prove that your security matters
Cyber attacks are not a hoax. Online crimes are steadily growing every year with millions of people falling victim to hackers, losing their personal data, and money. More than ever it begins to look like a game of cat and mouse. While the cybersecurity cat is getting smarter and agile, the hacking mouse still finds news ways to escape. We’ve gathered various data breach and hacking statistics to draw a detailed picture of just how prevalent cybercrime is.
Contents
Data breaches hit a new milestone
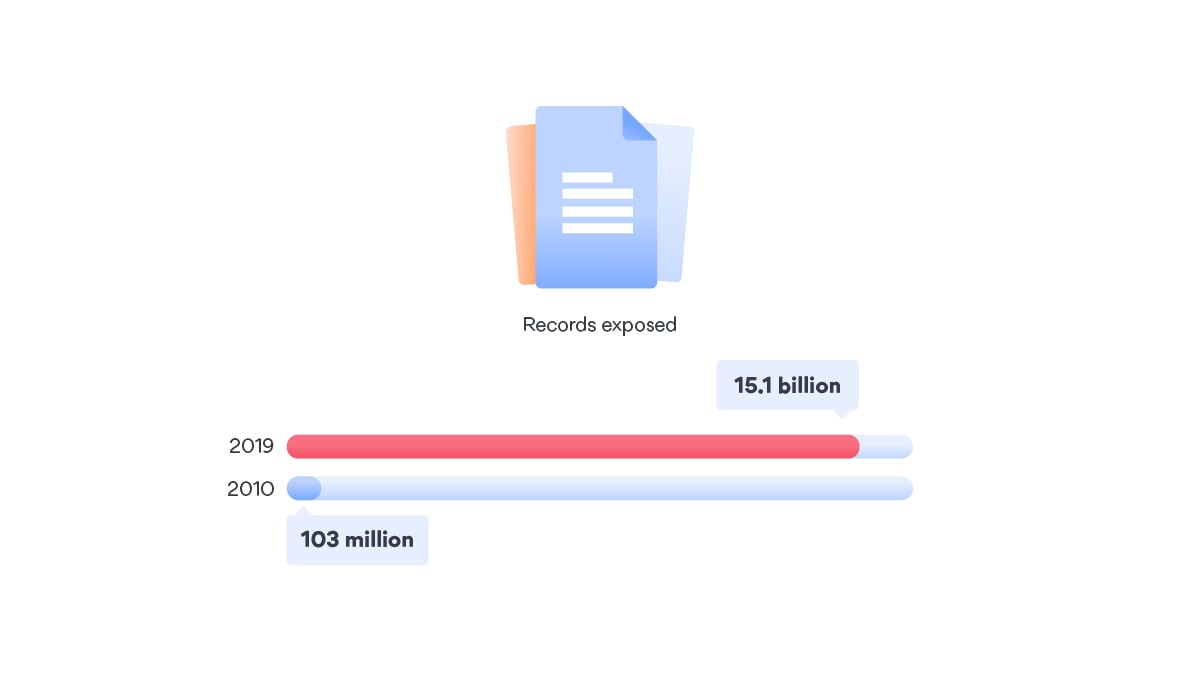
A startling 15.1 billion records were exposed in 2019, and that’s 284% growth compared with 2018. However, the number of data breaches only grew by 1%, which suggests that they may be becoming more effective (Risk Based Security).
The stats for 2019 may still change, as perpetrators sometimes put breached data up for sale on the dark web only months or years later. This makes it much harder for authorities to reveal the source of the hack and find the wrongdoers. It’s possible that a service you’re using has already been hacked and that the attackers are just waiting for the right time to cash in.
The biggest breach of 2019 affected 1.2 billion people. This vast collection of data, the majority of which was allegedly harvested by People Data Labs and Oxydata, was discovered on an unsecured server. It contained names, email addresses, phone numbers, and LinkedIn, and Facebook profile information — 4 billion records in total.
Other major leaks of 2019:
- Orvibo, a smart home technology company — 2 billion records
- TrueDialog, an SMS texting solutions provider — over 1 billion records
- First American Financial Corporation, financial services company — 885 million records
- “Collection #1”, the source of the breach is not identified – 773 million records (HIBP)
10 years ago, there were only 986 reported breaches with 103 million records exposed. The decade of growth in data breaches is incredible and it’s not slowing down.
How much does a data breach cost?
The average cost of a data breach is $3.86 million, however, this varies from country to country. Companies from the US suffer the most as the expenses can reach up to $8.64 million (IBM). However, everything depends on the scale of the hack and the size of the company.

In 2018, the personal details of about 500,000 British Airways customers were exposed, including names, email addresses, credit card numbers, their expiration dates, and CCV codes. For failing to comply with GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and to secure its customers, British Airways faces a record £183 million fine. They’re still fighting legal battles to this day and expect to reduce the final penalty to £22 million.
According to the IBM report, it takes 280 days on average to identify and contain a breach. Time is the most crucial factor in hacking incidents. Companies that were able to detect a breach in less than 200 days spent, on average, $1.1 million less on recovery.
However, the consequences of data breaches can chase companies for years, as only 61% of the cost comes in the first year. 24% comes in the next year, and the final 15% comes two years later. Not to mention the damaged reputation and loss of customers and revenue.
Developed countries are more vulnerable to cyber attacks
According to NordVPN’s Cyber Risk Index, developed countries are more likely to fall victim to cyber criminals. Countries like Denmark, Norway, or Sweden are popular among hackers not because of their poor digital security. High incomes, widespread smartphone usage, constant travelling, and frequent e-shopping makes the Nordics appealing targets.
India is considered to be the least risky country on the list as only 1 of 3 Indians use the internet. But that’s not the whole picture. If you look at Indians who use the internet, the risk of them getting hacked might be even higher than in some developed countries as they are very active online.
It is estimated that 20% of the global population have fallen victims to cyber criminals in some way.
Cybercrimes surged during COVID-19

While the world was coming together to fight the most vicious virus since the Spanish flu, cyber criminals used COVID-19 as an opportunity to scam the vulnerable. With an unprecedented amount of people working from home and public panic, it was woefully easy.
In March 2020, online scams increased by over 400% compared with previous months, making the virus one of the biggest cybersecurity threats ever. The cyber attacks have come in various forms, such as phishing, malicious links, email compromise, malware, ransomware, and fake landing pages (ReedSmith).
In April, Google announced that they were blocking 18 million phishing and malware emails every day related to COVID-19. The scams impersonated various government and health organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO). While 99,9% of these emails never reached their recipients, many people still fell into the hackers’ traps.
With the rise of remote work during national quarantines, Zoom, an enterprise communication service, saw a spike in new users. However, Zoom was also criticized for its weak security. Around 530,000 Zoom user accounts were found for sale on the dark web, containing usernames, passwords, email addresses, host keys, and personal meeting URLs.
Researchers analyzed 1.2 million newly observed host names in March and April and found out that 86,600 were high-risk or malicious (Palo Alto’s Unit 42). The United States made it to the top of the list (29,007), followed by Italy (2,877), Germany (2,564), and Russia (2,456). “In every crisis, there is an opportunity” — a famous proverb says. Hackers are clearly familiar with the concept.
Ransomware statistics
Ransomware occurs when hackers encrypt your data and demand a ransom to get it back. It’s nasty business, but business is good. While cybersecurity experts discourage people from paying the criminals, many still do.

A report says that 1 out of 4 organizations have paid their ransom and the majority got their data back. However, there are always some cases when hackers refuse to unlock the files even after being paid (Sophos).
Differences between countries are also significant. In India, 66% of organizations paid the ransom, while in Spain only 4% chose to meet hackers’ demands. 56% of companies worldwide restored their data using backups. This only proves how important it is to be prepared for the worst.
Ransomware attack techniques:
- A file download/email with a malicious link — 29%
- Remote attack on server — 21%
- Email with malicious attachment — 16%
- Misconfigured public cloud — 9%
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) — 9%
- Via a supplier who works with an organization — 9%
- Via a USB/removable media device — 7%
Windows users should be worried the most as they faced 87% of all ransomware attacks, with macOS facing just 7%. One of the most notorious ransomware attacks, WannaCry, infected 200,000 Windows OS computers in 150 countries. Users were asked to pay $300-$600-worth in Bitcoin to get their data back. National Health Service hospitals in England and Scotland were hit the hardest, with 70,000 devices affected. As of today, WannaCry is still active and running.

How much does a ransomware attack cost?
In 2019, the Baltimore City government was hit by ransomware and was demanded to pay $76,000 in Bitcoin. The attack crippled public services and the estimated recovery cost is believed to be around $18 million.
However, FedEx, a delivery company, suffered even more. In 2017, FedEX was hit by a ransomware attack called NotPetya. It disrupted the company’s operations and caused $300 million in losses.
Ransomware facts
- There were 188 million ransomware attacks in 2019 (Statista).
- In 2020, an attack against a hospital in Germany lead to the first-ever ransomware-related death.
- $10 billion is the estimated cost of NotPetya ransomware.
- In 2017, 19,000 appointments were cancelled in one week when WannaCry ransomware hit the UK’s National Health Service.
Phishing statistics
Phishing is a scam technique to obtain sensitive information from people by sending fake emails or text messages. Hackers pretend to be from reputable companies and try to manipulate you to click on malicious links.

Reports say that 88% of organizations around the world experienced phishing attacks in 2019 with healthcare and manufacturing being among the highest-risk industries (Verizon). However, phishing attacks also target individuals. The more phishing emails a hacker sends, the more likely somebody will click on a malicious link and download their malware.
Here’s a list of the most frequently impersonated brands (Check Point):
- Apple
- Netflix
- Yahoo
- PayPal
- Chase
- Microsoft
- eBay
- Amazon
When you receive an email from Amazon or Facebook asking to change your password or renew credit card details, you hardly expect it to be a phishing attempt. But this is what hackers do. In the surge of COVID-19, hackers changed their targets and Zoom became the most impersonated brand.
Some hackers, however, like to get more personal. 65% of perpetrators used spear phishing (Symantec), which means that they research their target before conducting their attack. This might include information extracted from data breaches, social media accounts, or anything they can find online.
While many internet users believe they will never fall for a phishing attack, one study paints a different picture — 38% of users who don’t undergo cyber awareness training fail phishing tests (KnowBe4).
How much does a phishing attack cost?
The FBI’s report says that, between June 2016 and July 2019, there were over 166,000 phishing incidents. The victims lost $26 billion worldwide, with US citizens leading the list with $10 billion in losses across 69,000 victims.
It is believed that a new phishing site launches every 20 seconds, which just proves the scale of these attacks.
Even tech giants can fall victim. Between 2013 and 2015, scammers stole over $100 million from Google and Facebook. They impersonated a company from Taiwan, created fake email accounts, and sent invoices to Google and Facebook’s employees. While it seems like a simple scheme, nobody raised an eyebrow when they made money transfers to the fake company.
Phishing facts
- 30% of phishing emails are opened by targeted users (Verizon).
- 58% of phishing websites use SSL/TLS and HTTPS to make them look more legitimate (APWG).
- 15% of people that fell victim to phishing scams will be targeted at least one more time within a year (Retruster).
- PDFs and Microsoft Office files are used the most in phishing attacks.
- 96% of spear phishing attacks are motivated by intelligence gathering (Symantec).
Malware statistics
Malware is malicious software that can serve different purposes: to steal your data, monitor your browsing activity, or damage your device. Virus, worms, spyware, adware, ransomware — all of these are examples of malicious software.
94% of malware is delivered by email (Verizon). For many years, macOS was considered to be resistant to malware, but things are changing. With the growing popularity of Apple devices, macOS dedicated malware cases have increased by 400% in the last few years. Windows still holds the biggest piece of malware pie, however, with 84% of all reported cases.
With the growing popularity of IoT devices, hackers have shifted their focus. Computer crime statistics show that there were 25 million IoT malware attacks in 2019, with 75% of them targeting routers. Experts predict that, by the end of 2025, a staggering 75 million IoT devices will be operating worldwide, which will attract hackers even more.

Countries with the most malware attacks, in millions (Statista):
- United States — 5,093
- China — 602
- United Kingdom — 584
- Canada — 432
- India — 412
To understand how quickly malware can spread, look no further than ILOVEYOU. In 2000, this virus spread like wildfire, sending itself to everyone in the victim’s email list, overwriting files, and causing systems to crash. Estimates say that 10% of the world’s computers were infected, including the CIA, Pentagon, the British Parliament, and large corporations.
Malicious apps can mask their intentions and even make it to official stores like Google Play or the App Store. In March 2020, 56 malicious applications were discovered on Google Play with 1.7 million downloads altogether. They were masking themselves as calculators, recipes, translation apps, and racing games.
Cyberattack statistics by year (the amount of malware infections in millions):
- 2009 – 12.4
- 2010 – 29.97
- 2011 – 48.17
- 2012 – 82.62
- 2013 – 165.81
- 2014 – 308.96
- 2015 – 452.93
- 2016 – 580.40
- 2017 – 702.06
- 2018 – 812.67
How much do malware attacks cost?
The average cost of a malware attack for a company is $2.6 million (Accenture), making it the most expensive type of cybercrime. The cost involves:
- Business disruption
- Information loss
- Revenue loos
- Equipment damage
Malware facts
- 1 in 13 web requests lead to malware (Symantec).
- 51.45% of all malware is attributed to Trojans (PurpleSec).
- Cybersecurity experts believe that ⅓ of the world’s computers are infected.
- 350,000 new malicious programs and potentially unwanted applications are discovered every day (AV-TEST).
- There are 980 million malicious programs (SonicWall).
DDoS statistics
What can you do with an IP address? Launch a DDoS attack against it, for one thing. DDoS (distributed denial of service) attacks occur when hackers clog the victim’s network or device with traffic, slowing down services they’re targeting or even making them crash. Experts predict that DDoS attacks will double from 7.9 million in 2018 to 15.4 million by 2023 (CISCO).
During a DDoS attack, it can be responsible for as much as ¼ of a country’s internet traffic.
Industries most often targeted by DDOS attacks (Imperva):
- Games — 35,9%
- Gambling — 31,3%
- Computers and internet — 26,5%
- Business — 3,4%
- Finance — 3%
In 2015, a British hacker left all of Liberia without internet access after a successful DDoS attack. He was hired by Cellcom, a Liberian telecom operator, to launch a series of attacks on a rival telecom company called Lonestar. Lonestar lost tens of millions of dollars in revenue as a result.
How much does a DDoS attack cost?
DDoS attacks could cost up to $120,000 for a small company and $2 million or more for an enterprise. You can buy a week-long DDoS attack on the dark web for as little as $150. Considering the damage it creates, this is a real bargain!
DDoS facts
- The longest DDoS attack lasted for 13 days and peaked at 292,000 requests per second (Imperva). Usually, DDoS attacks don’t last more than 15 minutes.
- ⅔ of DDoS attacks are distributed from China.
- Some of the biggest companies that suffered DDoS attacks include GitHub, Dyn, BBC, Bank of America, and JP Morgan Chase.
- 12% of businesses believe that their rivals launched DDoS attacks against them (Kaspersky).
- 2000 attacks are registered every day (ATLAS threat report).
Must-know cybersecurity statistics & facts

How to protect yourself from cyber attacks
- Use strong passwords and regularly change them. Your password should contain special symbols and numbers, along with lowercase and uppercase letters. For the maximum security, we recommend using a password manager such as NordPass.
- Update your software. Hackers always search for software vulnerabilities and bugs. Updates improve security and prevent you from becoming a victim of a cyber attack.
- Avoid suspicious links. If a website you visited or an email you just got looks shady, probably it is shady. Don’t click on any links or pop-ups and leave such websites immediately.
- Use a VPN. VPN (virtual private network) masks your IP address and encrypts traffic, thus protecting your online privacy and making your safer online. NordVPN is an easy-to-use app, which will mitigate the risk of ending up in hacking statistics. With the cyber attacks on the rise, a VPN is a necessary tool for anyone who enjoys streaming movies, gaming, or just browsing online.
- Back up your files. While hackers can lock you out from your data and ask for ransom, backups might save you money.
- Use additional security tools. NordVPN’s Threat Protection feature is a great way to enhance your security. It will scan the files you download for malware and prevent you from visiting malicious websites.
Don’t become another statistic. Enhance your security with a top-notch VPN.