How to check if your VPN is working
Not sure if your VPN is working? The easiest way to tell if your VPN connection is working as expected is to run a VPN test. Check your IP address before and immediately after connecting to the VPN. In this post, we’ll explain how to check if a VPN is working, so you can ensure you’re properly connected.
Contents
How to tell if a VPN is working
There are several different ways to check that your VPN service is working properly and protecting your internet traffic and personal data.
- Check your IP address. Take note of your current IP address, connect to a VPN server, and recheck the IP address. If it differs from the one you initially noted, your VPN works.
- Check for DNS leaks. Domain name system (DNS) leaks happen when a VPN fails to encipher your DNS traffic, and your DNS queries go through to your ISP’s DNS servers.
- Check for WebRTC leaks. Every browser has a built-in Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) protocol for real-time communication.
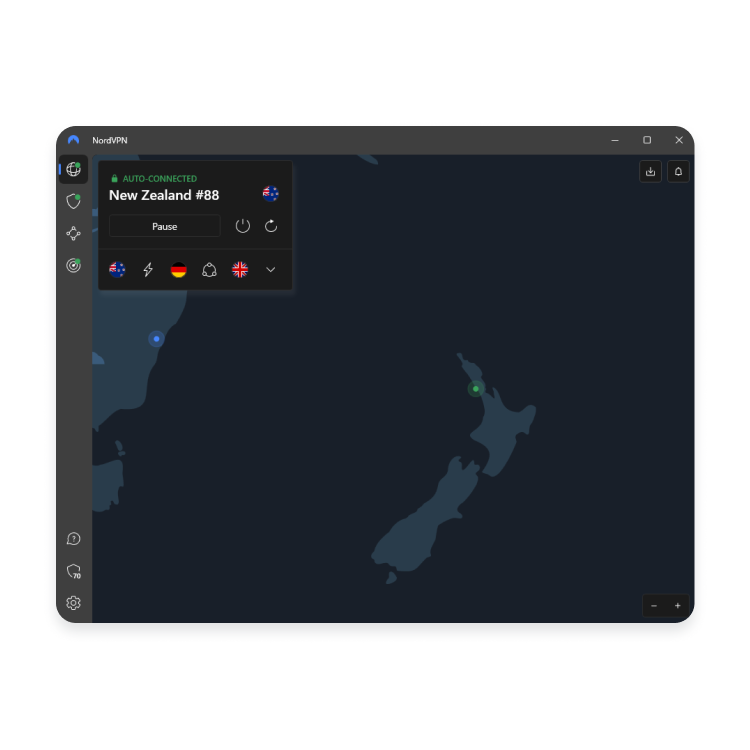
- Check your VPN status. Most VPN software shows if you are connected to a VPN. Make sure your status is “Connected.”
- Test your internet speed. Connect to a VPN and run an internet speed test. If the internet speed is lower than usual, there might be some issues.
Follow the instructions to find out more about how running occasional VPN tests is important to ensure the effectiveness, performance, and security of a VPN, safeguarding your privacy and sensitive data.
Test a VPN for IP address leaks
Your IP address says a lot about you, like your location or the websites you visit. A VPN protects you from snoopers trying to access this information, so if your original IP leaks, it defeats the purpose of using a VPN. This usually happens due to two internet protocols, IPv4 and IPv6, and their incompatibility. Once someone has your real IP address, it will allow them to monitor your online behavior.
How to check if your IP address is leaked
Checking if your VPN is leaking your real IP address takes only a few simple steps:
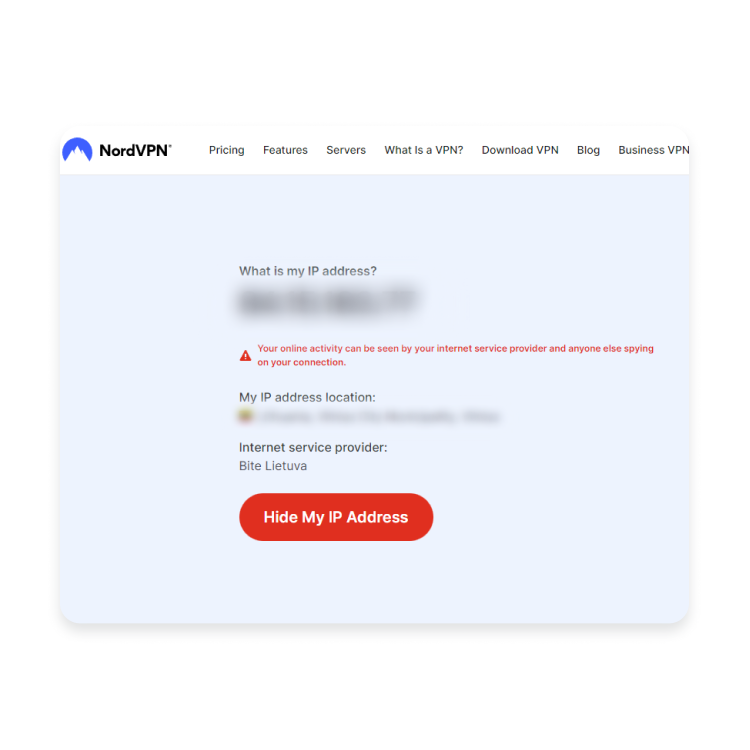
- Check your original IP address. Ensure your VPN is turned off and head to “What is my IP address?” page, which will show your IP.

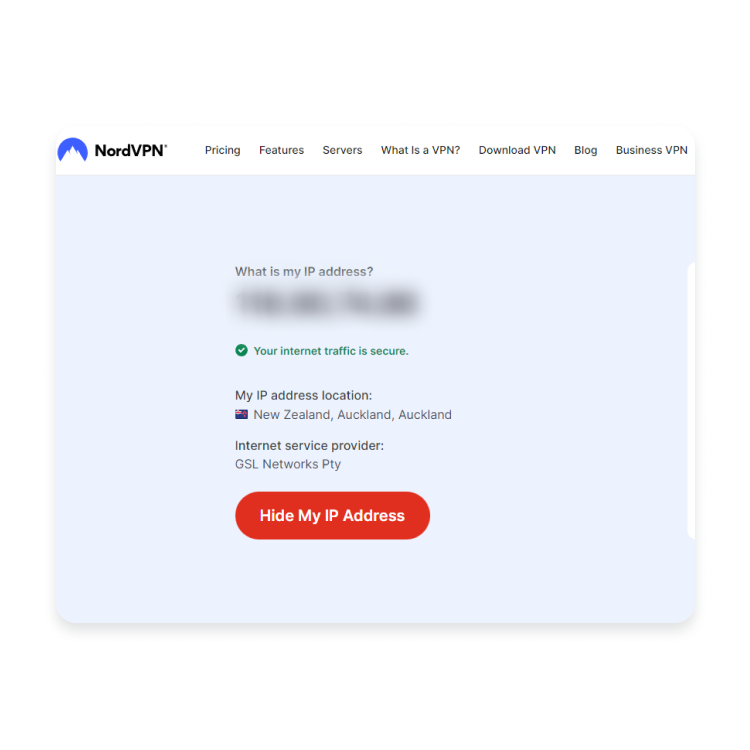
- Turn on your VPN and connect to a server. Now, your IP address should change to one of the VPN providers.

- Compare your virtual IP address against your actual IP. Head to the test page again to see if your IP is different. Unfortunately, if the results show your original IP address with a VPN enabled your VPN leaks.

How to fix IP address leaks
While detecting an IP address leak is pretty simple, there might be multiple reasons causing it. Unintentionally enabled split tunneling, your web browser settings, or specific apps or services might interfere with your VPN connection. For example, your antivirus software or additional proxies used together with a VPN may compromise the integrity of your network.
Choosing a reliable VPN service provider to prevent an IP leak is also very important. There are multiple factors that you should be aware of when choosing a trustworthy VPN, but in terms of IP address leak prevention, here are a few things to look for in a VPN:
- Strong DNS protection.
- Reliable WebRTC protection.
- A VPN kill switch that disconnects your device from the internet if the VPN connection is lost or interrupted.
Choosing a reputable VPN provider now can prevent unpleasantness later, so choose responsibly and don’t use shady or free VPNs.
Online security starts with a click.
Protect your IP from potential leaks with NordVPN
Test a VPN for DNS leaks
Sometimes your IP address might stay hidden while your DNS address secretly reveals your location. The DNS server changes plain text URLs into numerical IP addresses. If you’re not using a VPN, this process is handled by your internet service provider (ISP) and their servers, which can see who visited what websites. If your DNS leaks, anyone snooping on your traffic will be able to access this information too. It could even lead to a DNS hijacking attack.
How to check if your DNS has leaked
Sometimes, IP leak tests fail to detect DNS leaks, which can also reveal some information about you. So it’s advisable to check it on our DNS leak test page:
- If your VPN is on, the DNS leak test page should show your chosen location and your new IP address.
- If your VPN is on, but the results show your actual IP address and location or DNS servers are different from those your privacy tool provides, you may have a DNS leak.
How to fix DNS leak
Whether you want to fix or prevent DNS leaks, there are several steps you can take:
- Choose a secure VPN provider with dedicated and private DNS servers and built-in DNS leak protection.
- Run occasional VPN scans with VPN check tools. This will help you identify if your VPN connection is secure and protected against potential security threats.
- You could manually turn IPv6 off on your device. However, this might require some technical know-how.
Test a VPN for WebRTC leaks
WebRTC allows a website or app to provide video and audio communications and even some file-sharing services without extra software. A WebRTC leak is when your browser inadvertently reveals your actual IP address when using WebRTC services. A robust VPN with up-to-date security protocols typically prevents WebRTC leaks, although not all VPNs have that capability.
How to check for WebRTC leaks
WebRTC is built into the most popular browsers (i.e., Firefox, Opera, Chrome, and Brave), so it’s recommended to run occasional tests for leaks. Here’s how to do it:
- Connect to your VPN, preferably choosing a country other than the one you’re in, and visit browserleaks.com.
- Find the “WebRTC leak test” field. Does it show your new IP address and location based on your chosen country? Then you’re good to go. If it shows your original IP address and actual location, you have a WebRTC leak.
How to fix a WebRTC leak
Changing your VPN server or tinkering with your settings won’t help this time. However, you can:
- Use a browser that doesn’t have WebRTC. If you wonder, here is a complete list of browsers that exclude WebRTC.
- Manually disable WebRTC in your browser.
Test your VPN speed
You need to run a VPN speed test to check your VPN speed. You can try Speedtest to evaluate your VPN speed. Here’s how to do it:
- Turn on your VPN and choose a server.
- Run a speed test.
- Turn off your VPN, run the speed test again, and note the difference.
The smaller the speed difference, the less it affects your internet speed.
Remember – many factors determine VPN speed, such as your overall internet speed, the distance between you and your VPN server, and your VPN protocol. So if you are unsatisfied with your VPN speed, you can try changing VPN servers or protocols.
Test if your VPN connection is blocked
Some websites restrict access for VPN users and may ask you to turn off your VPN in order to reach the site. This may be a problem when you are traveling, for example, and want to access your home content.
If you cannot access your preferred website while connected to a VPN, try changing to an obfuscated server or your own dedicated IP address. If connecting to a different VPN server allows you to access previously unreachable websites, your VPN works perfectly.
Test a VPN for malware
Here are a few steps you can take to ensure your VPN program doesn’t contain any malware:
- Choose a secure VPN. Check your VPN provider’s reputation before purchasing a service. Read some reviews and comments, and check its privacy policy, no-logs policy, and encryption methods to ensure the VPN is trustworthy.
- Get anti-malware software. Before installing your VPN software, make sure you use updated anti-malware software, which detects and prevents malicious software from infecting your device.
- Use a sandbox environment. Test your VPN in a sandbox environment first. Checking software in an isolated environment may protect your device from potential malware.
- Monitor your network activity. Check your network for suspicious activity while using a VPN. If you see something fishy, disable the VPN immediately and run a malware scan.
Why is my VPN connected but not working?
If you’ve performed all of these tests and you still can’t connect to a VPN, there may be other reasons why it might seem that your VPN isn’t working:
- Your connection is unstable. Check if your firewall or other security tools doesn’t interfere with your VPN network.
- Your browsing speed has dropped. A slower browser speed is a sign of connecting to a server on the other side of the world, the server is overloaded, or your ISP is throttling bandwidth. However, you can check and increase your VPN speed with a few simple tricks.
- Your ISP or your country is blocking VPN usage. In some countries, especially with online censorship, VPN usage can be blocked or considered illegal. In China, for example, only government-approved VPNs are legal.
- VPN malware. Technology experts would never recommend using free VPN apps. Not only do most contain intrusive ads, but some also contain malware. If using a free VPN, you may be exposing more personal information than you wanted to.
- VPN settings. Check your VPN settings and ensure you are connected to the correct VPN protocol, server, and port.
- You’ve been hacked. It takes a lot of work to break into someone’s secure online account and requires a suitable amount of know-how. It’s more likely that you’ve visited a malicious website or fallen for a phishing attack. Unfortunately, if someone hacks you, a VPN can’t do much to protect you.
- Contact your VPN provider. If none of the above solutions work, contact your VPN service provider for help.
What to do if your VPN isn’t working
Sometimes your VPN connection drops for no discernable reason, or your VPN speed might be slow. Here are a few tips for solving your VPN issues:
- Reset your VPN app. This is probably the most obvious advice, but resetting your VPN can do miracles. Switch off the app, use the Force Stop function on your phone if necessary, and restart.
- Change a VPN protocol. If you’re experiencing connectivity issues, try changing from UDP to TCP protocol in your VPN app.
- Hop between servers. A slow VPN network might suggest that something’s wrong with the server you’ve connected to. Change to another server and see if your VPN works better.
- Check your internet connection. Unstable Wi-Fi may also be why your VPN service is not working. You can connect your device directly to a router to get more speed or contact your ISP.
- Update your VPN software. Keep your software updated because it can help you fix VPN issues and provide the latest security and privacy features.
- Check your firewall settings. Your firewall might block your VPN traffic, preventing you from connecting to the server. Try disabling your firewall temporarily to see if this is the problem.
- Talk to technical support. If you still need help understanding what’s wrong with your VPN, contact technical support, usually available 24/7, and they will help you solve issues.